| Sudden Cardiac Arrest | Heart Attack | |
| Definition | SCA is a chaotic electrical condition of the heart resulting in the loss of blood flow to the brain and body. The most common form of SCA is ventricular fibrillation. | The medical term for a heart attack is myocardial infarction: a blockage of the coronary arteries leading to a decrease in blood flow.When this happens, the heart muscles die or become permanently damaged. |
| Causes | Electrical impulses of the heart become chaotic due to a blow to the chest or other (sometimes-unknown) health-related issues. As a result, the heart stops beating regularly and begins to flutter rapidly. | Plaque made of cholesterol and other cells builds up in the walls of the heart’s arteries.When the buildup is great enough, the plaque creates a blockage, known as an occlusion, which restricts the blood supply to the heart muscle. |
| Symptoms | Typically, there are no symptoms to SCA. Usually, the first indication of SCA is when the victim faints. The second sign is breathing cessation. | Warning signs of heart attack include a tightening feeling in the chest, a sore or numb left arm, lower back, neck, and/or jaw.Other signs include bad indigestion, a feeling that something heavy is sitting on your chest, and shortness of breath. |
| Victim's Response | A sudden cardiac arrest victim always loses consciousness from lack of oxygen. | The victim of a heart attack is usually conscious and alert. |
| Risk of Death | A victim of SCA will die unless treated. If left untreated, the chances of survival decrease by 10% per minute.Typically, permanent brain damage occurs within 5-7 minutes. | Most victims can recover fully and lead normal lives, but about a third of heart attacks are deadly. A heart attack can lead to sudden cardiac arrest. |
| Treatment | The only treatment for SCA is defibrillation from an automated external defibrillator (AED). A shock from the AED stops the chaotic electrical activity and allows the heart's sinus node to resume a normal electrical impulse. | One treatment of a heart attack can be angioplasty, which opens up the blocked vessels with a medical balloon. Afterwards, a stent can be placed in the artery to help keep it open.Other treatments include clot-busting drugs called thrombolytics or nitroglycerin to reduce chest pain. |
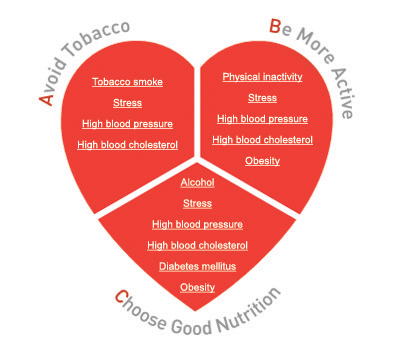
So, remember this information, and most of all, remember the ABCs of heart care: Avoiding Tobacco, stress and fatty foods, Being more active andChoosing the right nutrition and life style that will keep your heart healthy!
Some materials submitted by: venkatachalam p
 - A heart attack often causes chest pain.
- A heart attack often causes chest pain. Pain in the abdomen
Pain in the abdomen
No comments:
Post a Comment